Agricultural crops :: Cereals :: Ragi diseases
| Blast: Pyricularia grisea |
Symptom:
- Infects at any stage of the growth from the seedling to the grain formation stage
- The infection appears in the nursery from second week of germination and spread quickly to entire nursery as well as to main field.
- Small brown circular to elongated spots appear on leaves which eventually develop into large elongated spindle shaped areas in the seedling stage. Young leaves dry completely in the nursery itself
- The spindle shaped spots appear on leaves in the main field. Several spots coalesce and cause drying of foliage
- Maximum damage is caused by the neck blast. The neck region turns black and shrinks.
- Infection occurs at the basal portions of the panicle branches including the fingers and the ear head breaks away from the stalk. The affected portions turn brown and ears become chaffy and only few shriveled grains are formed
- Some of the fingers are also affected causing finger blast. The fingers become chaffy and only few shriveled grains are formed
|
| |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
| |
INFECTED PLANT |
|
BLAST ON LEAF |
|
FINGER BLAST |
|
Identification of pathogen:
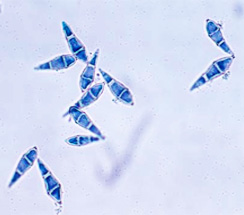
- Mycelium is intra and inter-cellular
- Numerous conidiophores and conidia are produced in the central portion of the spindle shaped spots under humid conditions. As a result, the spot assumes a smoky appearance
- Conidiophores emerge through the stomata or through the epidermal cells are simple septate and dark coloured
- Conidia are borne at the tip of the conidiophores
- Conidia are pyriform, 3 celled, hyaline, 2 septate
- Conidia germinate with germ tubes which infect the leaf wither through epidermal cells or stomata
|
| |
 |
|
 |
|
|
| |
Pyricularia grisea |
|
Conidia of Pyricularia grisea |
|
|
|
| MANAGEMENT: |
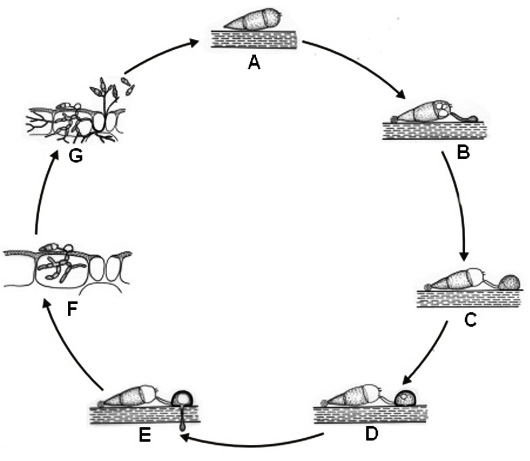
Life cyle of Pyricularia grisea |
|
|
Cultural method
- Use disease free seeds
- Grow resistant varieties like CO RA (14), Paiyur (RA)-2, GPU-28, GPU-45,GPU-48, L-5
- Proper plant spacing and transplanting is advisable
- Early sowing (July month) reduces the blast severity
Biological method
- Spray Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf1) at 2 g/lit of water. First spray immediately after noticing the symptom. Second and Third sprays at flowering stage at 15 days interval
- Treat the seed with Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 6g/Kg seed and spray the extracts of Prosopis juliflora leaf extract (10%), Ipomoea carnea leaf extract (10%)
- Foliar spray with premixture fungicide (Carbendazim+Mancozeb) @ 0.2% concentration at 50% earhead emergence followed by a second spray with Pseudomonas fluorescens (Pf1) at 2g/lit of water 10 days later
Chemical method
- Seed treatment with carbendazim @ 1 gm/Kg of seed
- Spray Carbendazim 0.1% in nursery 10-12 days after sowing. Repeat the spray 20-25 days after transplanting and 40 to 45 days after transplanting
- Spray any one of the fungicides Carbendazim 500 g or Iprobenphos (IBP) @ 500 ml/ha or premixture fungicide (Carbendazim+Mancozeb) @ 500g/ha. First spray immediately after noticing the symptoms. Second and third sprays at flowering stage at 15 days interval to control neck and finger infection.
|
 |
|
Source of lifecyle: http://www.ibwf.de/funagro_index.htm
Content Validator: Dr. T.Raguchandar, Professor (Plant Pathology), TNAU, Coimbatore-641003
Thanks to Dr.M.N.Budhar, Professor and Head, Regional Research Station, Paiyur- 65112 |
|






